- #1
Titan97
Gold Member
- 450
- 18
From the resonance structures of Naphthalene, 1-2 Bond has more double Bond character than 2-3 Bond.
In March's Advanced organic chemistry, its given that ozone preferentially reacts with 1-2 Bond. But the reaction is not given. Is this a normal ozonolysis reaction in which the 1-2 Bond is broken and replaced with a carbonyl group? (Like the reaction of ethene with ozone to form formaldehyde)
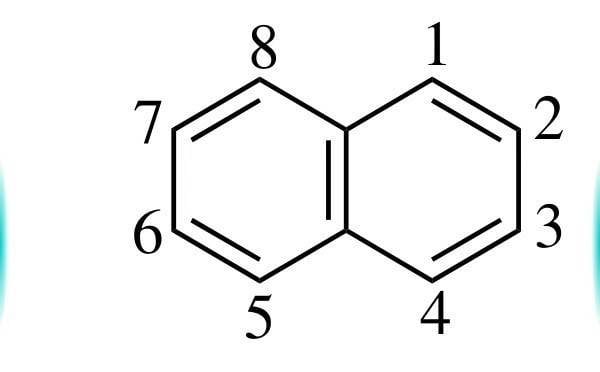
In March's Advanced organic chemistry, its given that ozone preferentially reacts with 1-2 Bond. But the reaction is not given. Is this a normal ozonolysis reaction in which the 1-2 Bond is broken and replaced with a carbonyl group? (Like the reaction of ethene with ozone to form formaldehyde)