- #1
Stephanus
- 1,316
- 104
Dear PF Forum,
Lunar Satelite orbits the moon,
The moon orbits the earth,
The Earth orbits the sun,
I know that some of you know about this picture
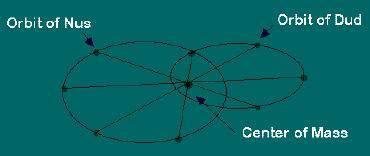
You might want to tell me. "No Steven, the Sun also orbits the earth"
But for all practical purpose, we'd say that the earth orbits the sun. So does the moon, the moon satelite, etc
Okay, so I'l continue.
The sun orbits the SMBH in the centre of our galaxy.
And in turn, what Milky Way orbits to?
Considering Hubble Law, that every galaxy is moving away each other.
Does Milky way somehow orbits a bigger galaxy,
And if it's true how many galaxies orbit that thing?
And what thing that that thing orbits?
And in that sense what is the last thing that doesn't orbit anything, if there is such last thing.Thank you very much
Lunar Satelite orbits the moon,
The moon orbits the earth,
The Earth orbits the sun,
I know that some of you know about this picture
You might want to tell me. "No Steven, the Sun also orbits the earth"
But for all practical purpose, we'd say that the earth orbits the sun. So does the moon, the moon satelite, etc
Okay, so I'l continue.
The sun orbits the SMBH in the centre of our galaxy.
And in turn, what Milky Way orbits to?
Considering Hubble Law, that every galaxy is moving away each other.
Does Milky way somehow orbits a bigger galaxy,
And if it's true how many galaxies orbit that thing?
And what thing that that thing orbits?
And in that sense what is the last thing that doesn't orbit anything, if there is such last thing.Thank you very much