- #1
dsdsuster
- 30
- 0
I'm confused by the fact that for the typical non-inverting amplifier,
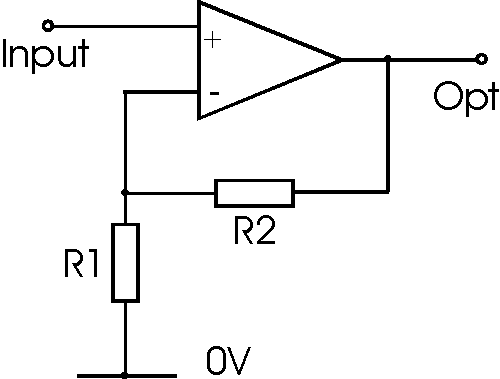
(1) The input current is ideally 0 A.
but
(2) The current going into ground is given by Vin/R1 where R1 is the resistor above ground.
If Vin were provided by a battery for example, which has Voltage=0V on one side and Vin on the other doesn't this imply that the current isn't steady and charge is building up inside the battery?
Thanks!
(1) The input current is ideally 0 A.
but
(2) The current going into ground is given by Vin/R1 where R1 is the resistor above ground.
If Vin were provided by a battery for example, which has Voltage=0V on one side and Vin on the other doesn't this imply that the current isn't steady and charge is building up inside the battery?
Thanks!