- #1
Happiness
- 679
- 30
I believe there is a mistake in the second equation of (5.139).
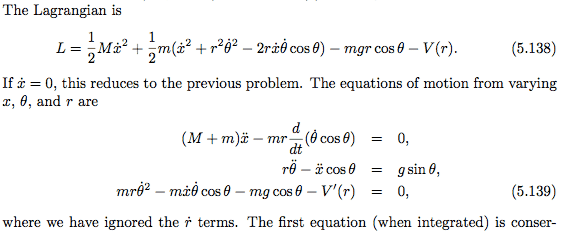
The equation is obtained from (5.138) using the Euler-Lagrange equation
##\frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot{\theta}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial\theta}.##
LHS##\,\,=\frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot{\theta}}=\frac{d}{dt}(mr^2\dot{\theta}-mr\dot{x}\cos\theta)##
##=mr^2\ddot{\theta}-mr\dot{x}(-\sin\theta)\dot{\theta}-mr\ddot{x}\cos\theta\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,## (Note that ##\dot{r}## terms are ignored.)
RHS##\,\,=mgr\sin\theta##
Equating LHS and RHS, and dividing by ##m## and ##r##, we have
##r\ddot{\theta}+\dot{x}\sin\theta\dot{\theta}-\ddot{x}\cos\theta=g\sin\theta##.
Am I right?
The equation is obtained from (5.138) using the Euler-Lagrange equation
##\frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot{\theta}}=\frac{\partial L}{\partial\theta}.##
LHS##\,\,=\frac{d}{dt}\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot{\theta}}=\frac{d}{dt}(mr^2\dot{\theta}-mr\dot{x}\cos\theta)##
##=mr^2\ddot{\theta}-mr\dot{x}(-\sin\theta)\dot{\theta}-mr\ddot{x}\cos\theta\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,## (Note that ##\dot{r}## terms are ignored.)
RHS##\,\,=mgr\sin\theta##
Equating LHS and RHS, and dividing by ##m## and ##r##, we have
##r\ddot{\theta}+\dot{x}\sin\theta\dot{\theta}-\ddot{x}\cos\theta=g\sin\theta##.
Am I right?