- #1
ATY
- 34
- 1
Hey guys,
I need your help.
We tried to derive the ekman transport in a lecture. The assumptions we made are
1. constant density
2. stationarity
3. no horizontal pressure gradient and no horizontal velocity gradient
4. no vertical velocity.
So this is what the professor showed us:
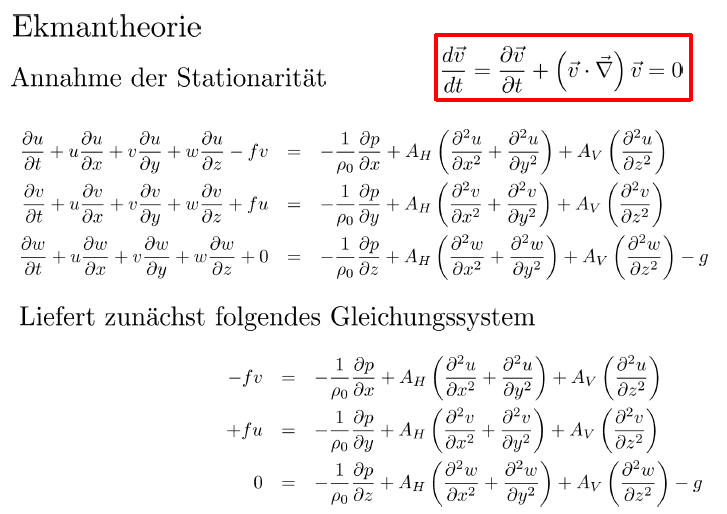
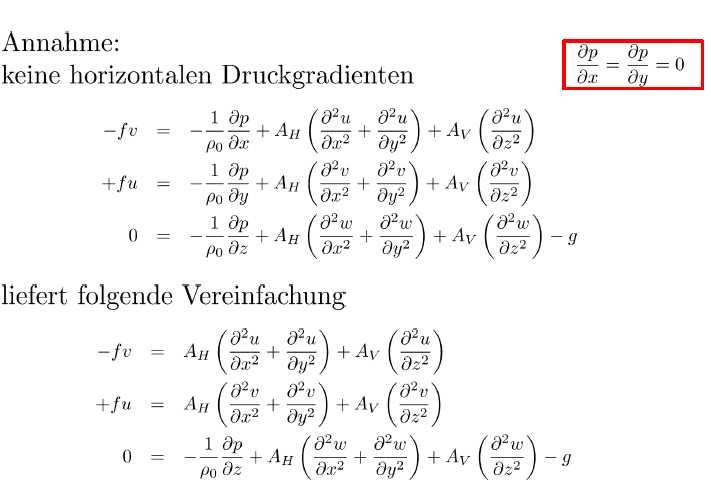
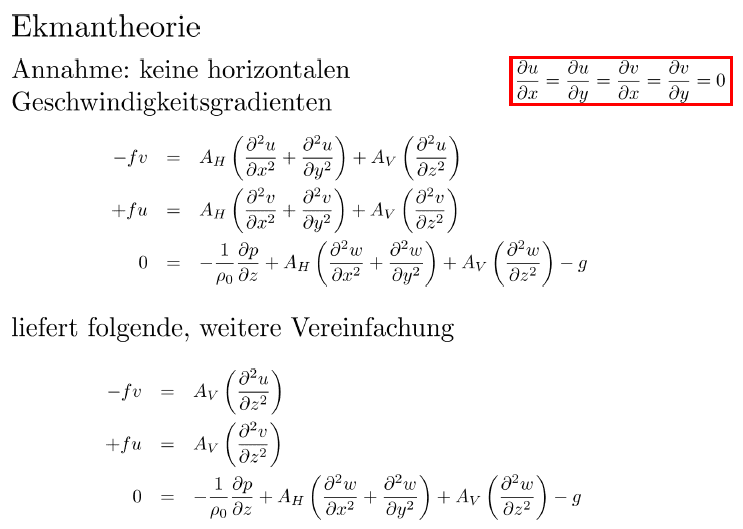
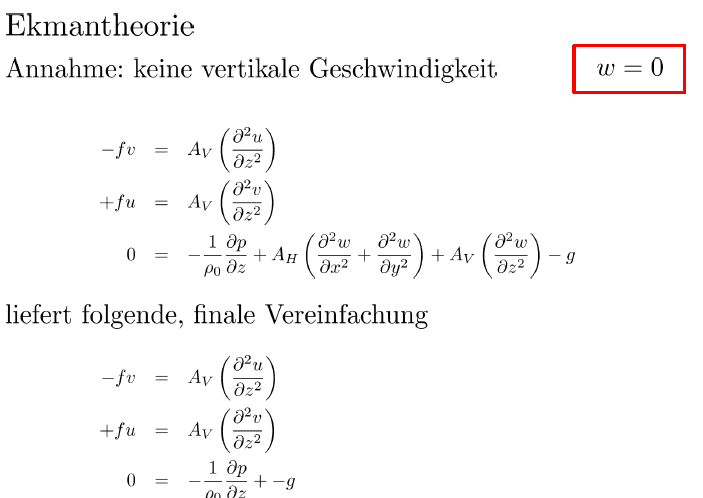
But is this correct ? I thought that from stationarity we get [itex]\frac{\partial}{\partial t}=0[/itex] instead of [itex]\frac{d}{dt} = 0[/itex].
I would still get to the correct result using
[itex]\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}=0[/itex] and [itex]w=0[/itex] in order to eliminate all terms on the left side of the equation.
Can somebody help me ?
I need your help.
We tried to derive the ekman transport in a lecture. The assumptions we made are
1. constant density
2. stationarity
3. no horizontal pressure gradient and no horizontal velocity gradient
4. no vertical velocity.
So this is what the professor showed us:
But is this correct ? I thought that from stationarity we get [itex]\frac{\partial}{\partial t}=0[/itex] instead of [itex]\frac{d}{dt} = 0[/itex].
I would still get to the correct result using
[itex]\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}=\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}=0[/itex] and [itex]w=0[/itex] in order to eliminate all terms on the left side of the equation.
Can somebody help me ?