- #1
Amith2006
- 427
- 2
Sir,
I am posting these questions for the 3rd time as you didn't respond. Please respond.
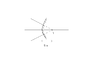
1)A convergent beam of light is incident on a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm as shown in figure. What is the nature and position of the image formed by it?
I solved it in the following way:
Let u, v and f be the object distance, image distance and focal length of the convex mirror respectively.
Here u = + 10 cm, f = +30 cm
1/u + 1/v = 1/f
v = (uf)/(u-f)
= (10 x 30)/(10 – 30)
= -15 cm
Hence the image formed is virtual and 15 cm in front of the mirror. Is it right?
2)A convex mirror of focal length f produces an image (1/n)th of the size of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
I solved it in the following way:
Magnification = 1/n = -(v/u)
i.e. v = -(u/n)
1/u + 1/v = 1/f
1/u – (n/u) = 1/f
By solving I get,
u = (1-n)f
Are my sign conventions right? Sometimes the diagram may not be clear. So I will try to describe the diagram. A convergent beam of light serves as a virtual object which appears to converge at a distance of 10 cm behind the mirror.
I am posting these questions for the 3rd time as you didn't respond. Please respond.
1)A convergent beam of light is incident on a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm as shown in figure. What is the nature and position of the image formed by it?
I solved it in the following way:
Let u, v and f be the object distance, image distance and focal length of the convex mirror respectively.
Here u = + 10 cm, f = +30 cm
1/u + 1/v = 1/f
v = (uf)/(u-f)
= (10 x 30)/(10 – 30)
= -15 cm
Hence the image formed is virtual and 15 cm in front of the mirror. Is it right?
2)A convex mirror of focal length f produces an image (1/n)th of the size of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
I solved it in the following way:
Magnification = 1/n = -(v/u)
i.e. v = -(u/n)
1/u + 1/v = 1/f
1/u – (n/u) = 1/f
By solving I get,
u = (1-n)f
Are my sign conventions right? Sometimes the diagram may not be clear. So I will try to describe the diagram. A convergent beam of light serves as a virtual object which appears to converge at a distance of 10 cm behind the mirror.