- #1
CylonBaby
- 8
- 0
A mass m = 6.2 kg hangs on the end of a massless rope L = 1.96 m long. The pendulum is held horizontal and released from rest.
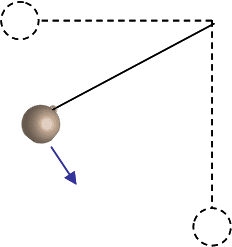
1) How fast is the mass moving at the bottom of its path?
I calculated this to be 6.201 m/s using the equation v=√(2gh) (correct)
2) What is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the bottom of the path?
Calculated value 182.457 using T=mg+mv^2/r (correct)
3) If the maximum tension the string can take without breaking is Tmax = 509 N, what is the maximum mass that can be used? (Assuming that the mass is still released from the horizontal and swings down to its lowest point.)
Calculated value: 17.296 using a rearranged version of above formula: m= T/(g+v^2/r) (correct)
4)
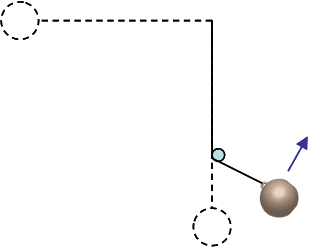
Now a peg is placed 4/5 of the way down the pendulum’s path so that when the mass falls to its vertical position it hits and wraps around the peg. As it wraps around the peg and attains its maximum height it ends a distance of 3/5 L below its starting point (or 2/5 L from its lowest point).
How fast is the mass moving at the top of its new path (directly above the peg)?
On this one I used the chg in PE equation and multiplied the result by 3/5 PE=mgh(3/5) to give me the Kinetic Energy (since it is a conservative force)and KE=-PE
I got 71.5267 J and set up another equation KE = 1/2 mv^2
rearranging to solve for v I get v= √(KE*2/m)
I got 4.803 m/s (correct)
5) Using the original mass of m = 6.2 kg, what is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the top of the new path (directly above the peg)?
I have tried a few things using the new velocity, but I am not sure which values to keep and which to chuck at this point. Any pointers are helpful.
1) How fast is the mass moving at the bottom of its path?
I calculated this to be 6.201 m/s using the equation v=√(2gh) (correct)
2) What is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the bottom of the path?
Calculated value 182.457 using T=mg+mv^2/r (correct)
3) If the maximum tension the string can take without breaking is Tmax = 509 N, what is the maximum mass that can be used? (Assuming that the mass is still released from the horizontal and swings down to its lowest point.)
Calculated value: 17.296 using a rearranged version of above formula: m= T/(g+v^2/r) (correct)
4)
Now a peg is placed 4/5 of the way down the pendulum’s path so that when the mass falls to its vertical position it hits and wraps around the peg. As it wraps around the peg and attains its maximum height it ends a distance of 3/5 L below its starting point (or 2/5 L from its lowest point).
How fast is the mass moving at the top of its new path (directly above the peg)?
On this one I used the chg in PE equation and multiplied the result by 3/5 PE=mgh(3/5) to give me the Kinetic Energy (since it is a conservative force)and KE=-PE
I got 71.5267 J and set up another equation KE = 1/2 mv^2
rearranging to solve for v I get v= √(KE*2/m)
I got 4.803 m/s (correct)
5) Using the original mass of m = 6.2 kg, what is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the top of the new path (directly above the peg)?
I have tried a few things using the new velocity, but I am not sure which values to keep and which to chuck at this point. Any pointers are helpful.
Last edited: