- #1
octu
- 10
- 0
In the cable-pulley system shown here, block A is moving upwards at a speed of 5m/s and block C is moving downwards at a speed of 2.5m/s. What is the speed of block B? (See attached picture)
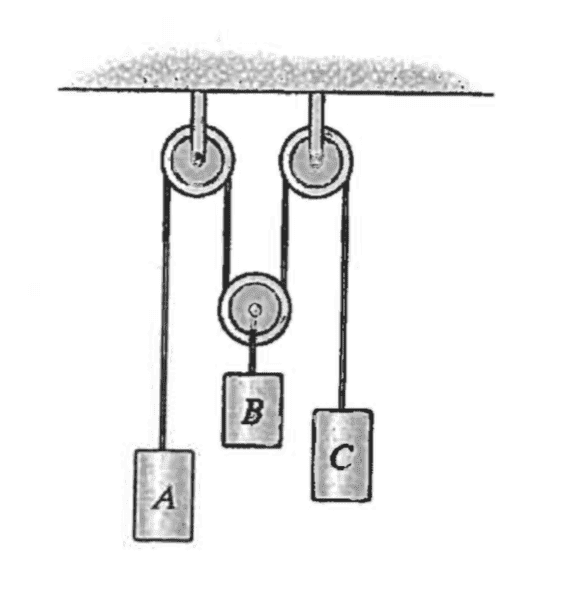
This seems easy, I just want to make sure I'm not crazy.
If mass B moves downward some distance d, then the string segments attached to B's pulley have both lengthened by d. Therefore, a total length of 2d must be subtracted from the sum of A and C's string lengths. If a, b, and c represent the mass's velocities, then we have:
-2b = a + c
Plugging in the values a = 5 and c = -2.5 (up is positive) gives b = -1.25m/s (downwards).
Correct?
This seems easy, I just want to make sure I'm not crazy.
If mass B moves downward some distance d, then the string segments attached to B's pulley have both lengthened by d. Therefore, a total length of 2d must be subtracted from the sum of A and C's string lengths. If a, b, and c represent the mass's velocities, then we have:
-2b = a + c
Plugging in the values a = 5 and c = -2.5 (up is positive) gives b = -1.25m/s (downwards).
Correct?