- #1
laser
- 75
- 10
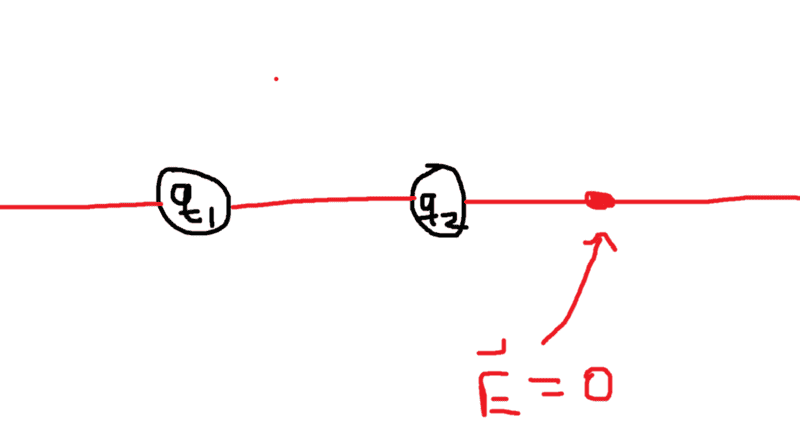
- Homework Statement
- E=0
- Relevant Equations
- Electric field is a vector
In many homework problems I've encountered, they all seem to assume the electric field = 0 point is along the axis of the two charges. Intuitively it kind of makes sense, but I'm looking for a solid justification for it. In other words, why can't it be off the axis of the two charges? When setting up the problem, everyone seems to just assume it is on the axis.
Couldn't find any information about this in the book/online. Thanks!
Couldn't find any information about this in the book/online. Thanks!