- #1
ampakine
- 60
- 0
I've read loads of explanations but can't find any that are detailed enough. Using a NPN bipolar transistor as an example:
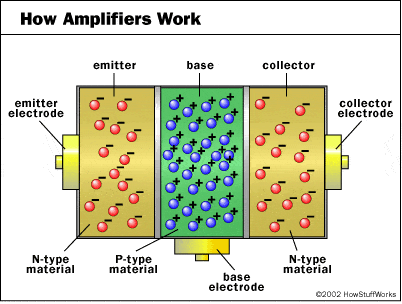
I know that the N type emitter and collector has a surplus of electrons and the P type base has a deficiency of electrons but I don't understand why current can't flow past the P type base. Wouldn't the electrons from the N type sections just occupy the holes in the P type section? Let's say that there are way more holes than surplus electrons, when the transistor is hooked up to a power source wouldn't the electrons from the negative terminal of the battery just fill in the remaining holes?
EDIT: Something I just thought of is the fact that the emitter and collector are both negatively charged to begin with so the negatively charged collector would repel the emitters electrons and oppose the flow of electrons across the base. In other words the base is kind of like a break in the circuit which is how the transistor acts as a switch. Have I got the right idea there? If so there's still a couple of things I don't get. 1.) if the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the collector then wouldn't the collectors surplus electrons just flow to the positive terminal of the battery? 2.) How do transistors act as amplifiers? Let's say I have a transistor hooked up to a 9V battery (the emitter connected to the negative terminal and the collector connected to the positive terminal). At first I have no current flowing through the base so no current can pass from emitter to collector. Then I apply say 500mA to the base which allows current to flow in the main circuit. Would that current be much greater than the current that would have been created by the 9V battery alone? If so, why?
I know that the N type emitter and collector has a surplus of electrons and the P type base has a deficiency of electrons but I don't understand why current can't flow past the P type base. Wouldn't the electrons from the N type sections just occupy the holes in the P type section? Let's say that there are way more holes than surplus electrons, when the transistor is hooked up to a power source wouldn't the electrons from the negative terminal of the battery just fill in the remaining holes?
EDIT: Something I just thought of is the fact that the emitter and collector are both negatively charged to begin with so the negatively charged collector would repel the emitters electrons and oppose the flow of electrons across the base. In other words the base is kind of like a break in the circuit which is how the transistor acts as a switch. Have I got the right idea there? If so there's still a couple of things I don't get. 1.) if the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the collector then wouldn't the collectors surplus electrons just flow to the positive terminal of the battery? 2.) How do transistors act as amplifiers? Let's say I have a transistor hooked up to a 9V battery (the emitter connected to the negative terminal and the collector connected to the positive terminal). At first I have no current flowing through the base so no current can pass from emitter to collector. Then I apply say 500mA to the base which allows current to flow in the main circuit. Would that current be much greater than the current that would have been created by the 9V battery alone? If so, why?
Last edited: