- #1
compound
- 5
- 0
In a package of a phosphor converted white LED (blue LED + Yellow phosphor), two heat generation mechanisms exist.
1. Joule heating at junction temperature of blue LED
2. Heat generation of the yellow phosphor layer due to stokes shift and blue light absorption.
Now I have questions.
1. Where is the hottest part in the LED package? junction or phosphor layer?
2. If
junction temperature = 100°C
generated temperature of phosphor layer = 30°C
then if i measure the temperature of the phosphor layer surface, what is the temperature? 130°C ?
(on the other words, thermal accumulation phenomenon is valid in the system?)
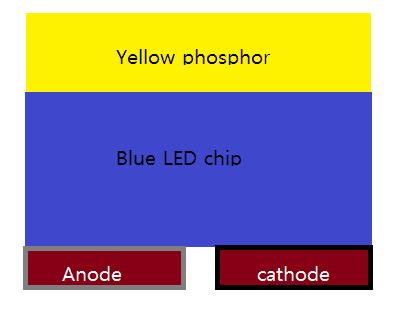
is their anybody expert for LED phosphor layer?
1. Joule heating at junction temperature of blue LED
2. Heat generation of the yellow phosphor layer due to stokes shift and blue light absorption.
Now I have questions.
1. Where is the hottest part in the LED package? junction or phosphor layer?
2. If
junction temperature = 100°C
generated temperature of phosphor layer = 30°C
then if i measure the temperature of the phosphor layer surface, what is the temperature? 130°C ?
(on the other words, thermal accumulation phenomenon is valid in the system?)
is their anybody expert for LED phosphor layer?