- #1
aladinlamp
- 44
- 1
Hi
is my assumption correct ?
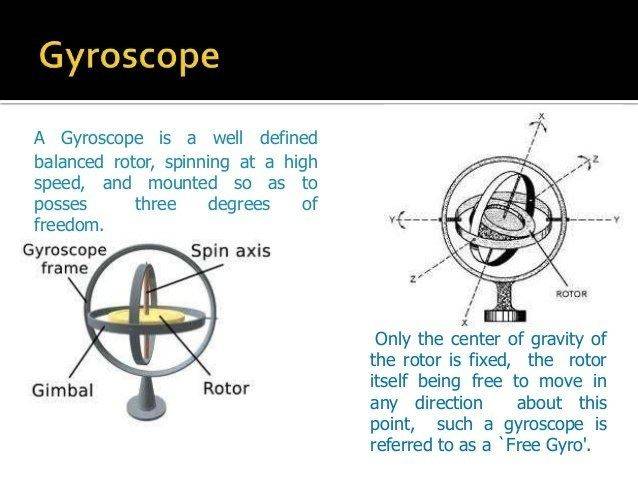
precision gyroscope,sitting on the table during 24 hours, perfectly balanced, with free motion in all 3 axis, while still spinning using electric drive or compressed air to maintain motion...
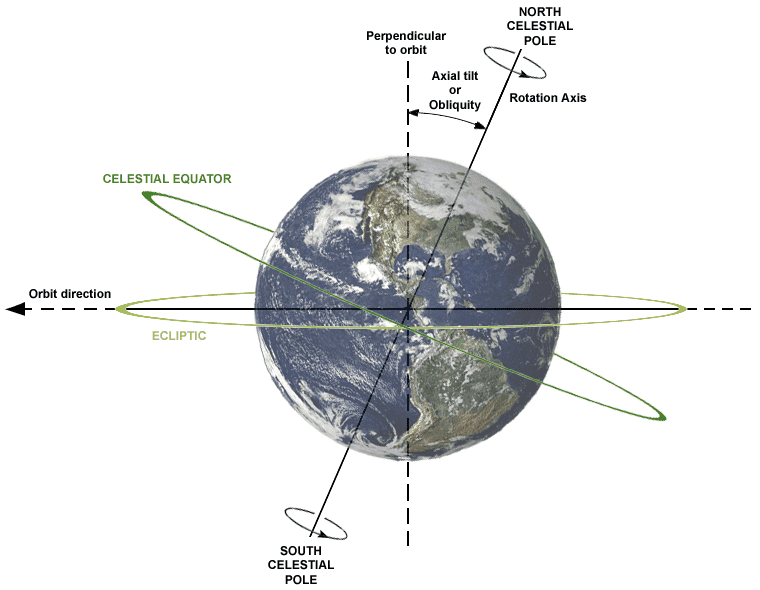
there should be relative motion between gyro and its stationary holder in all 3 axis( assuming I am not at the poles) but at some latitude less than 90.
gyro disk should keep orientation and holder will move with earth, but from my reference frame i will see holder stationary and gyro disk will move

is my assumption correct ?
precision gyroscope,sitting on the table during 24 hours, perfectly balanced, with free motion in all 3 axis, while still spinning using electric drive or compressed air to maintain motion...
there should be relative motion between gyro and its stationary holder in all 3 axis( assuming I am not at the poles) but at some latitude less than 90.
gyro disk should keep orientation and holder will move with earth, but from my reference frame i will see holder stationary and gyro disk will move