- #1
applestrudle
- 64
- 0
This is what I have so far:
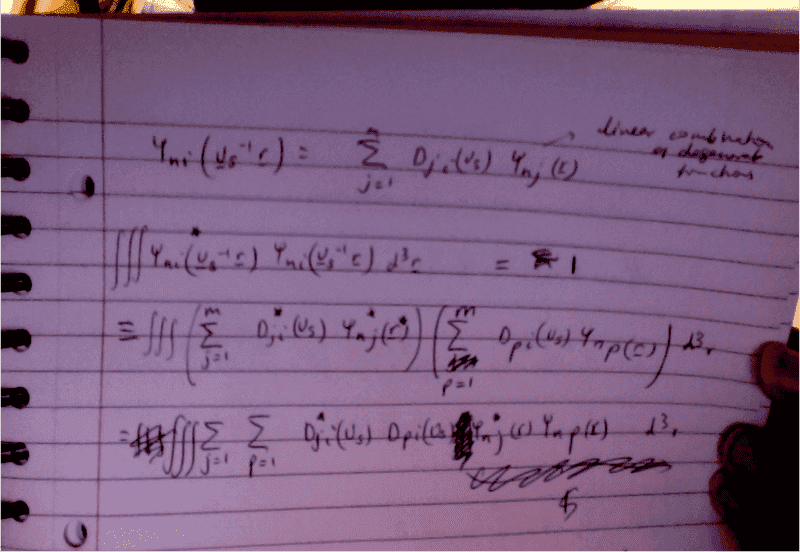
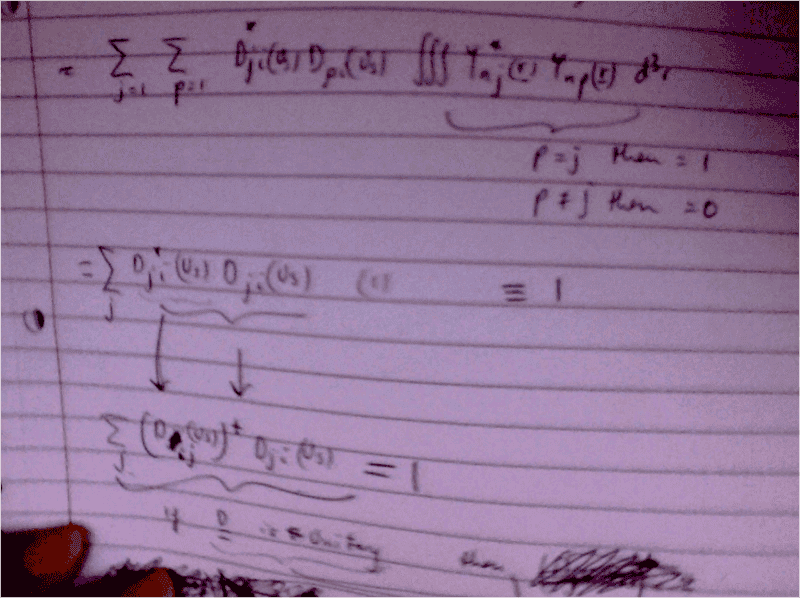
I'm trying to show that the matrix D has to be unitary. It is the matrix that transforms the wavefunction.
I'm trying to show that the matrix D has to be unitary. It is the matrix that transforms the wavefunction.