- #1
sel
- 1
- 0
Sorry if this ends up being a naive question, but I have just a little conundrum. I'm dealing with curves in R2 and the Gauss-Bonnet theorem is a very useful result with what I'm currently doing, what with Gaussian curvature of a flat surface being zero, which is all fine
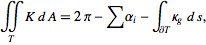
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Gauss-BonnetFormula.html
To proceed with my problem, I need to show that the geodesic curvature of a curve in R2 is the same as the standard curvature of it. I can sort of understand how it is the case from its definition but can't show it, if you know what I mean.
Thanks for all the help guys x
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Gauss-BonnetFormula.html
To proceed with my problem, I need to show that the geodesic curvature of a curve in R2 is the same as the standard curvature of it. I can sort of understand how it is the case from its definition but can't show it, if you know what I mean.
Thanks for all the help guys x