- #1
tylertwh
- 22
- 0
The velocity of an object at t=0 seconds is 40 m/s directed due North. The velocity of the same object at t=5 seconds is 30 m/s directed due east.
Find the magnitude of the average acceleration of the object over the time interval from t=0 to t=5 seconds.
Also, show the direction of the average acceleration. So... I am not quite sure how to even approach this problem. I originally tried it and did it with Pythagorean Theorem, but my answer was incorrect.
The answer I got using Pythagorean Theorem was 50 m/s at 36.9 East of North.
Please help!
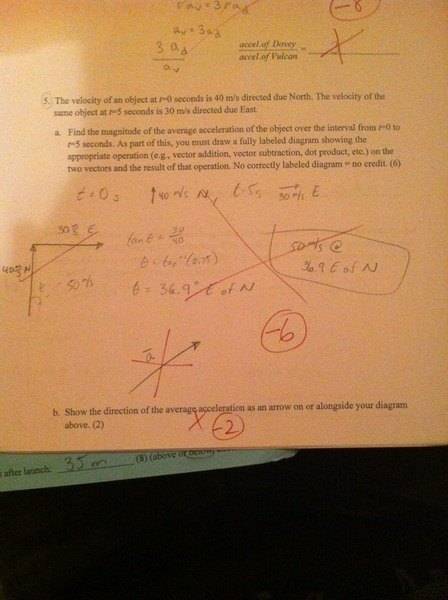
Find the magnitude of the average acceleration of the object over the time interval from t=0 to t=5 seconds.
Also, show the direction of the average acceleration. So... I am not quite sure how to even approach this problem. I originally tried it and did it with Pythagorean Theorem, but my answer was incorrect.
The answer I got using Pythagorean Theorem was 50 m/s at 36.9 East of North.
Please help!