- #1
tsuwal
- 105
- 0
My teacher said that instead of using a fiber optic made of just one material we could use a set of materials with progressively low refractive index to turn the light back in, like so:
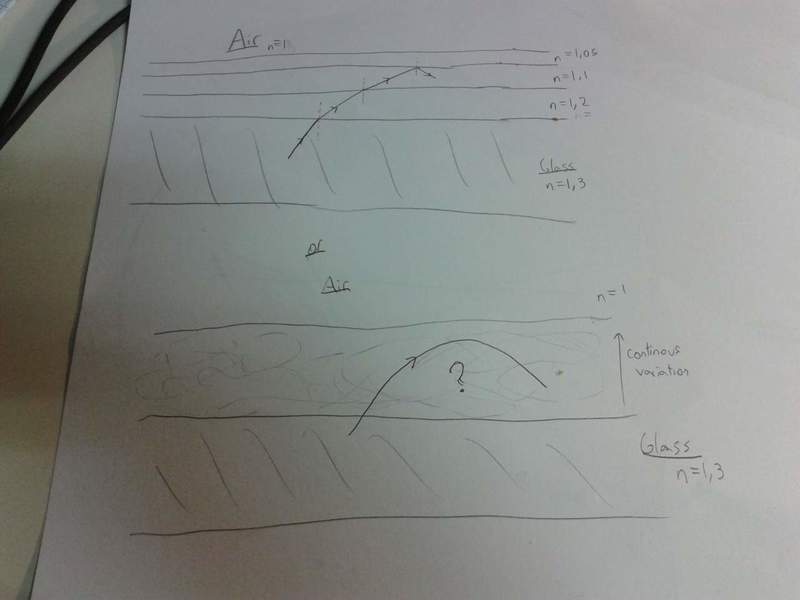
In the case of a continuous variation of refraction index, how can you do the math. Can you please show me, the right way for it?
In the case of a continuous variation of refraction index, how can you do the math. Can you please show me, the right way for it?