- #1
unscientific
- 1,734
- 13
For an EM wave close to the transition frequency ##\omega_{21}##, we assume the dipole moment to be exponentially damped and oscillating:
[tex] p(t) = p(0) e^{-\frac{\gamma}{2}t} cos(\omega_0 t) [/tex]
Why do we expect the electric field to be proportional to ##\dot p##?
Taken from my lecturer notes on laser and atomic physics:
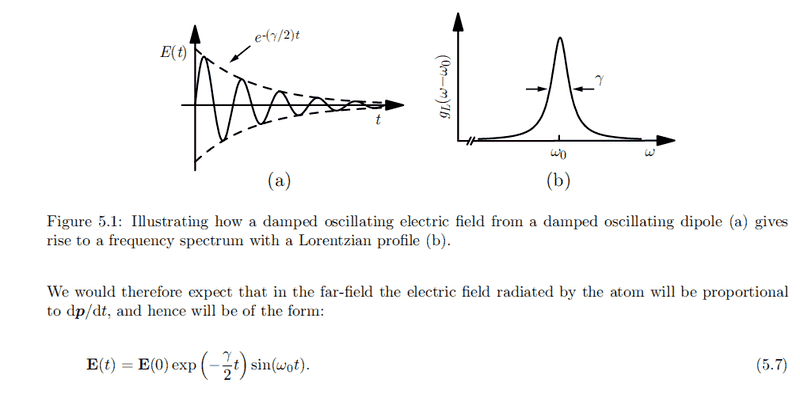
[tex] p(t) = p(0) e^{-\frac{\gamma}{2}t} cos(\omega_0 t) [/tex]
Why do we expect the electric field to be proportional to ##\dot p##?
Taken from my lecturer notes on laser and atomic physics: