- #1
student354
- 1
- 0
hi!
i asked to evaluate the schrodinger equation using dirac notaion.
i saw some ways but didn't understand them.
is it true?
if it does, what are M and 1 represent?
thanks!
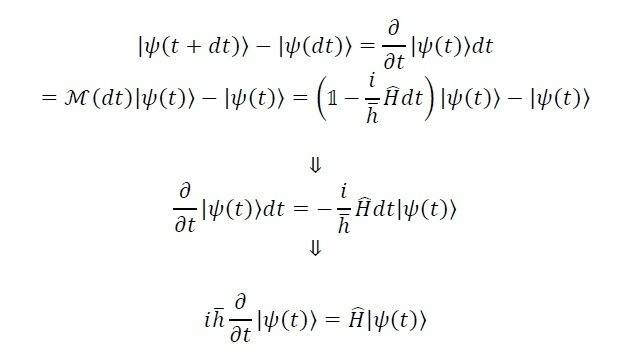
i asked to evaluate the schrodinger equation using dirac notaion.
i saw some ways but didn't understand them.
is it true?
if it does, what are M and 1 represent?
thanks!