- #1
Char-L
- 2
- 0
Hello dear physics masters on earth, I am very grateful to be priviliged to ask you a question regarding electric fields and potential of a single-cpin helix. It is portrayed as below.
It is a line of uniform charge, and 1-turn helix with radius R and height H. I have came to ugly answers, and I cannot verify whether I am right or wrong. I'm trying to calculate electric field and potential of a random point, assuming that the field is still applied on the point. I have tried to integrate electric field applied from a segment, which didn't turn out well. Any help would be gratefully appreciated. Thank you.
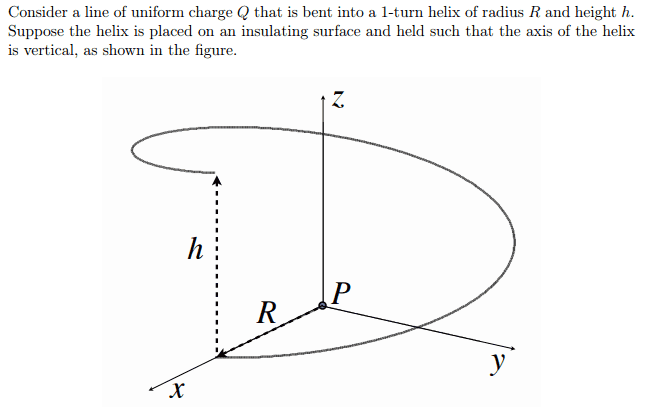
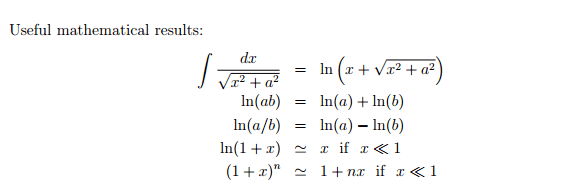
It is a line of uniform charge, and 1-turn helix with radius R and height H. I have came to ugly answers, and I cannot verify whether I am right or wrong. I'm trying to calculate electric field and potential of a random point, assuming that the field is still applied on the point. I have tried to integrate electric field applied from a segment, which didn't turn out well. Any help would be gratefully appreciated. Thank you.