- #1
elepolli
- 2
- 0
TL;DR Summary: I have a cantilever beam with fixed end, known rectangular cross section and total length h. A uniform load is applied on the beam from a distance L from the fixed end, to the free end. The E modulus and inertia I are known, and they are two different constant values for 0<x<L and L<x<0.
I want to know the deflection w(h) of the beam at the free end.
This is my approach, what do you think?



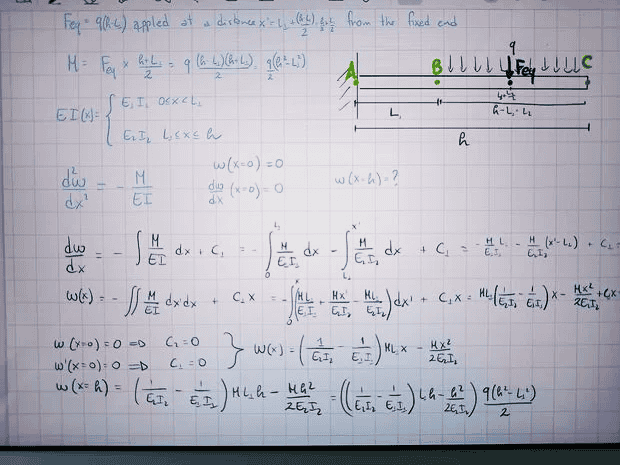

I want to know the deflection w(h) of the beam at the free end.
This is my approach, what do you think?



Last edited by a moderator: