- #1
bizuputyi
- 42
- 1
Homework Statement
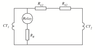
Determine RR value if the relay current has not to exceed 20mA. Neglect relay resistance.
2. The attempt at a solution
I believe the solution is behind Merz-Price theorem, where the voltage system is balanced. CT1 and CT2 are identical current transformers, however, RL2 (leads resistance) and RS2 (secondary winding resistance) upset the Merz-Price balance, therefore the need for RR I guess. The relay pulls in when current through it exceeds 20mA. RR is there to prevent unwanted relay operation (relay is to remain off under threshold current).
Now, without voltage and other resistance values I don't see the trick.
Is there a formula for this?
Thank you for your help.