- #1
student07
- 36
- 1
Examine the charge distribution shown:
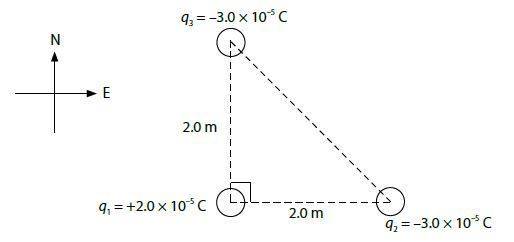
b) What is the net electric field acting on charge 1?
Attempt at the answer:
E2 = Kq2/r2^2 = (9.0 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2)(3.0 x 10^-5 C) / 2.0m^2
E2 = 6.75 x 10^4 N/C
E2 = E3 ( therefore, same procedure)
eNet = Sqr.rt. 6.75 x 10^4 N/C^2 + 6.75 x 10^4 N/C^2 = 9.55 x 10^4 N/C
angle = Tan^-1 = (6.75/6.75) = 45 deg.
The total electric field acting on charge 1 is 9.55 x 10^4 N/C [N 45deg. E]
Is this right?
b) What is the net electric field acting on charge 1?
Attempt at the answer:
E2 = Kq2/r2^2 = (9.0 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2)(3.0 x 10^-5 C) / 2.0m^2
E2 = 6.75 x 10^4 N/C
E2 = E3 ( therefore, same procedure)
eNet = Sqr.rt. 6.75 x 10^4 N/C^2 + 6.75 x 10^4 N/C^2 = 9.55 x 10^4 N/C
angle = Tan^-1 = (6.75/6.75) = 45 deg.
The total electric field acting on charge 1 is 9.55 x 10^4 N/C [N 45deg. E]
Is this right?