- #1
Rajveer97
- 6
- 0
Poster has been reminded to post schoolwork in the Homework Help forums
Hi everyone, first time poster here, I'm studying for a Materials exam, one of my weakest subjects and this question is causing me a lot of pain:
Beryllium (Be) is a HCP metal with an atomic weight of 9 g mol-1 , an atomic radius of 0.112nm and a density of 1850 kg m-3 . Calculate its c/a ratio given that Avogadro’s number is 6.02×1023 mole-1 .
Here's the working after some basic steps
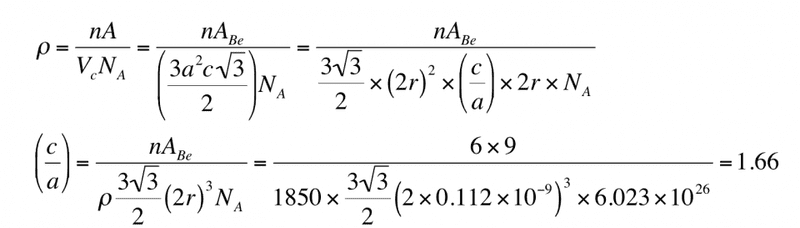
The thing that I don't understand is how this
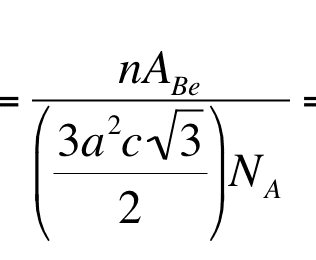
becomes this
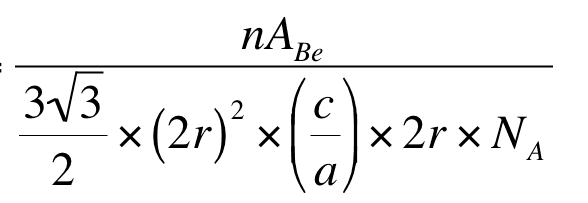
How are there two 2r there now? Where is the (c/a) coming from? I just can think through that, how does one get to that? Any help would be greatly appreciated I'm really stuck!
Thanks
Beryllium (Be) is a HCP metal with an atomic weight of 9 g mol-1 , an atomic radius of 0.112nm and a density of 1850 kg m-3 . Calculate its c/a ratio given that Avogadro’s number is 6.02×1023 mole-1 .
Here's the working after some basic steps
The thing that I don't understand is how this
becomes this
How are there two 2r there now? Where is the (c/a) coming from? I just can think through that, how does one get to that? Any help would be greatly appreciated I'm really stuck!
Thanks