- #1
physicsisfun0
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
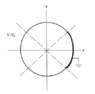
We have the cross section of a metal pipe that has been split into four sections. Three of the sections have a constant electric potential, Vo. The fourth section is grounded so electric potential is zero. We are looking for electric potential inside and outside of the pipe.
Homework Equations
For electric potential I have:
V = ao + boln(s) +Σ(sv(avcos(vφ) + bosin(vφ)) + s-v(cvcos(vφ) + dvsin(vφ))
We also know boundary conditions:
The Attempt at a Solution
(I think this next part is right)
And electric potential inside becomes:
V = ao + boln(s) +Σ(sv(avcos(vφ) + bosin(vφ))
And electric potential outside becomes:
V = ao + boln(s) +Σs-v(cvcos(vφ) + dvsin(vφ))
There is also symmetry along the x-axis so we can ignore the sin(vφ) contribution:
V = ao + boln(s) +Σ(sv(avcos(vφ))
V = ao + boln(s) +Σ(s-v(avcos(vφ))
Do I need to solve for ao and bo? How would I use the boundary conditions?