- #1
sltungle
- 27
- 0
1. Using the parametric solution of the Friedmann equations for a open, dust-filled universe
i) Calculate the radius of the Hubble sphere (RH) for a 'dust filled' open universe.
ii) Compare this with the radius of the particle horizon (Rp) for the same universe and determine if there exists a time when RH = Rp
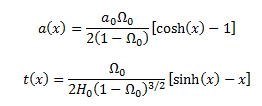
For part (i) I've used the fact that,
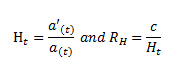
to attempt to determine RH.
Given that a is not in terms of t and the equations can't be rearranged to give a in terms of t I've opted to use the chain rule to determine a'(t)
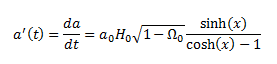
This is the correct way to proceed with the question (according to my lecturer).
Here's where I get confused though. Because t is already a function of x, do I simply use a(x) as my a(t)? That being, is the 't' in a(t) already accounted for by the fact that a(t) is actually (a(t(x))), or do I have to take da/dt, 'multiply' both sides of my equation by dt (don't get angry at me, pure mathematicians), and then integrate (where dt is actually dt(x)) to find a(t)?
To answer part (ii) I intended to find the equation for the particle horizon and then plot both functions (RH and Rp) on the same axes and check to see if there was ever an intercept, but I need to get RH correct in order to do that, so I'm not going to jump ahead of myself just yet. However, that said, just from the looks of things I don't think all of my Ω0 terms are going to drop out of the equation, so I'm not sure how I'm going to approach this if they stick around. I guess I might need to plot a 3D graph with x values, omega values, and respective RH and Rp values.
I apologise if this is a bit convoluted. I intended to use latex, but I'm not sure how to get it working on here.
i) Calculate the radius of the Hubble sphere (RH) for a 'dust filled' open universe.
ii) Compare this with the radius of the particle horizon (Rp) for the same universe and determine if there exists a time when RH = Rp
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
For part (i) I've used the fact that,
to attempt to determine RH.
Given that a is not in terms of t and the equations can't be rearranged to give a in terms of t I've opted to use the chain rule to determine a'(t)
This is the correct way to proceed with the question (according to my lecturer).
Here's where I get confused though. Because t is already a function of x, do I simply use a(x) as my a(t)? That being, is the 't' in a(t) already accounted for by the fact that a(t) is actually (a(t(x))), or do I have to take da/dt, 'multiply' both sides of my equation by dt (don't get angry at me, pure mathematicians), and then integrate (where dt is actually dt(x)) to find a(t)?
To answer part (ii) I intended to find the equation for the particle horizon and then plot both functions (RH and Rp) on the same axes and check to see if there was ever an intercept, but I need to get RH correct in order to do that, so I'm not going to jump ahead of myself just yet. However, that said, just from the looks of things I don't think all of my Ω0 terms are going to drop out of the equation, so I'm not sure how I'm going to approach this if they stick around. I guess I might need to plot a 3D graph with x values, omega values, and respective RH and Rp values.
I apologise if this is a bit convoluted. I intended to use latex, but I'm not sure how to get it working on here.
Last edited: