- #1
ace214
- 29
- 0
A 15.0-kg object is attached to a cord that is wrapped around a wheel of radius r = 9.0 cm (Fig. P8.60). The acceleration of the object down the frictionless incline is measured to be 2.00 m/s2. Assume the axle of the wheel to be frictionless.
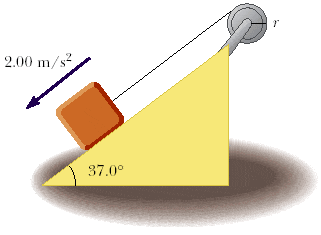
(a) Determine the tension in the rope.
58.46681 N
(b) Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel.
kg·m2
(c) Determine the angular speed of the wheel 2.00 s after it begins rotating, starting from rest.
rad/s
===================================
The tension is correct. I'm stuck on the inertia. I'll use 't' for torque and 'T' for the tension.
t=Iar => I = t/ar = Fr/ar = T/a but this doesn't work. I also tried using the force of gravity and the sigma force in the above equation and none of them are correct.Due tomorrow morning at 8:30 AM EST... :-(
(a) Determine the tension in the rope.
58.46681 N
(b) Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel.
kg·m2
(c) Determine the angular speed of the wheel 2.00 s after it begins rotating, starting from rest.
rad/s
===================================
The tension is correct. I'm stuck on the inertia. I'll use 't' for torque and 'T' for the tension.
t=Iar => I = t/ar = Fr/ar = T/a but this doesn't work. I also tried using the force of gravity and the sigma force in the above equation and none of them are correct.Due tomorrow morning at 8:30 AM EST... :-(
Last edited: