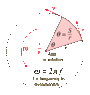- #1
Isolde Wilde
- 6
- 0
think of a engine. it has a flywheel and a rod connected to it. a string had been totally wrapped around the rod and a mass is hanged from the very end of the rod. the system is in equilibrium. but as the engine starts to rotate, the rod with rotate as well and cause the hanged object to go down while the string comes lose as the rod rotates. is the vertical velocity of the mass hanged equal to the angular velocity of the flywheel?