- #1
Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- See image attached below
- Relevant Equations
- dsin(theta) = m*lambda
Here is my problem

I have given this a go and get 26.77 degrees as my angular position
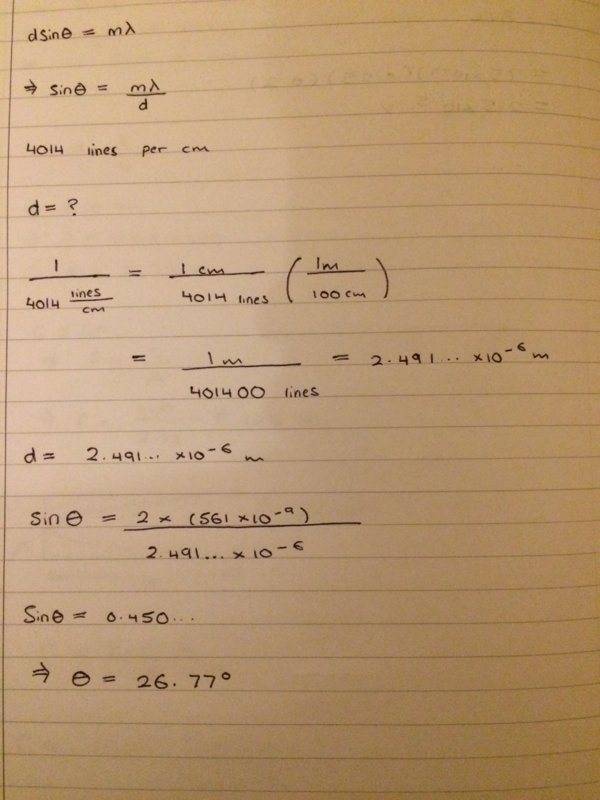
My concern is do I double this angle to get the angular width between both 2nd order maxima's (which would be 53.53 degrees) or do I just leave it as 26.77 degrees?
Thanks for any help!
I have given this a go and get 26.77 degrees as my angular position
My concern is do I double this angle to get the angular width between both 2nd order maxima's (which would be 53.53 degrees) or do I just leave it as 26.77 degrees?
Thanks for any help!