- #1
keropi452
- 3
- 0
Hi All,
Does anybody know how to solve the following PDE? I tried a similarity solution method where eta = y/f(x) (which I can do successfully without the C * U term) but was unsuccessful.
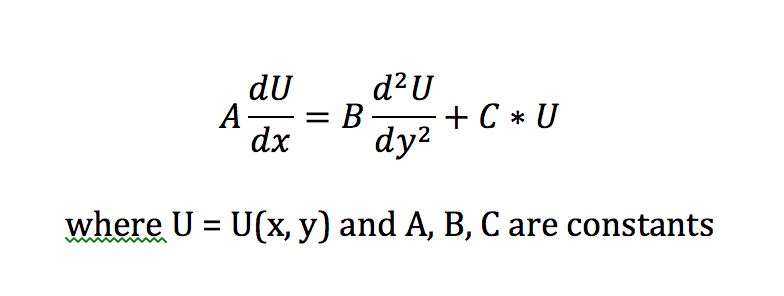
Thank you very much in advance!
Does anybody know how to solve the following PDE? I tried a similarity solution method where eta = y/f(x) (which I can do successfully without the C * U term) but was unsuccessful.
Thank you very much in advance!