- #1
baby_1
- 159
- 15
Hello
I'm getting confused when I want to use magnetic boundary equation
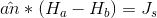
could you tell me how we define the unit vector(an) in this equation?
for example you assume that we have two different region (A in red and B in yellow) which vector (1,2,3,4) is right for
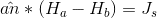 equation and which is right for
equation and which is right for
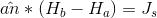 too?
too?
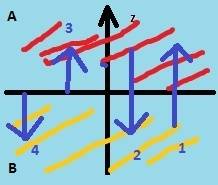
Thank you
I'm getting confused when I want to use magnetic boundary equation
could you tell me how we define the unit vector(an) in this equation?
for example you assume that we have two different region (A in red and B in yellow) which vector (1,2,3,4) is right for
Thank you