- #1
denfaro
- 8
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Almost Done.
- Relevant Equations
- T=p*e
Hi I am confused in this question. What Can I do after the steps in second photo?

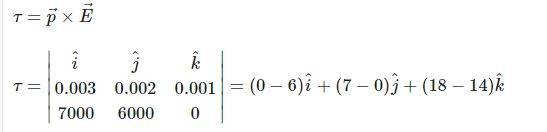
I think you are done: you have calculated the torque, which is what the exercise asked...denfaro said:What Can I do after the steps in second photo?
##\dots## except for the units.BvU said:I think you are done: you have calculated the torque, which is what the exercise asked...

Torque on two different-sign charged objects is the measure of the twisting force that is exerted on the objects due to the interaction of their opposite electrical charges. It is a rotational force that causes the objects to rotate around a point.
The torque on two different-sign charged objects is calculated using the formula T = r x F, where T is the torque, r is the distance between the objects, and F is the force of attraction or repulsion between the objects. The direction of the torque is perpendicular to the plane formed by the two objects.
The torque on two different-sign charged objects is affected by the magnitude of the charges, the distance between the objects, and the dielectric constant of the medium between the objects. The dielectric constant determines the strength of the electric field between the objects, which in turn affects the force of attraction or repulsion between them.
The direction of the charges affects the direction of the torque. If the charges are opposite, the torque will be in one direction, while if the charges are the same, the torque will be in the opposite direction. This is because the force of attraction or repulsion between the charges is also in opposite directions.
The torque on two different-sign charged objects is significant in understanding the behavior of charged particles in an electric field. It is also important in practical applications such as electric motors, where the torque is used to rotate a shaft. Additionally, torque can be used to measure the strength of an electric field and the magnitude of charges on objects.