- #1
Ascendant78
- 328
- 0
Ok, I'm trying to simulate a circuit containing a diode and I am a bit confused. I thought the arrow direction on the diode symbol shows which direction the current is able to flow through it. However, in my simulation, it is showing that the diode is limiting current flow in the exact opposite direction. Here are the images
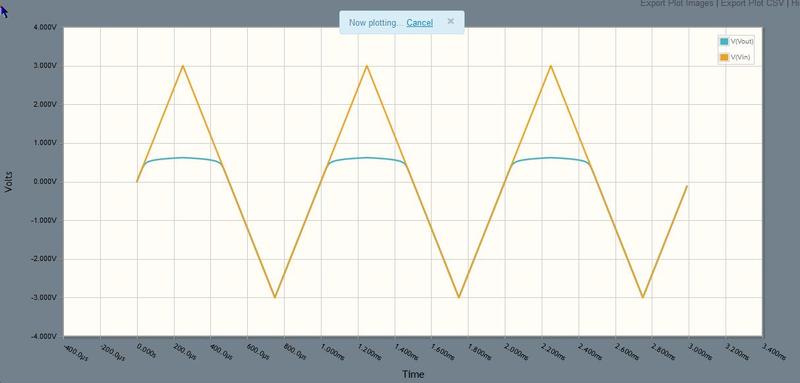
Can someone please make sense of this to me? Do diodes actually block current in the direction of the arrow on their symbol? This just doesn't seem right to me.
Can someone please make sense of this to me? Do diodes actually block current in the direction of the arrow on their symbol? This just doesn't seem right to me.