- #1
Goodver
- 102
- 1
What is a purpose of a substrate in an electronic device? In particular semiconductor lasers, why is it made of semiconductor?
Thank you.
Thank you.
Last edited:
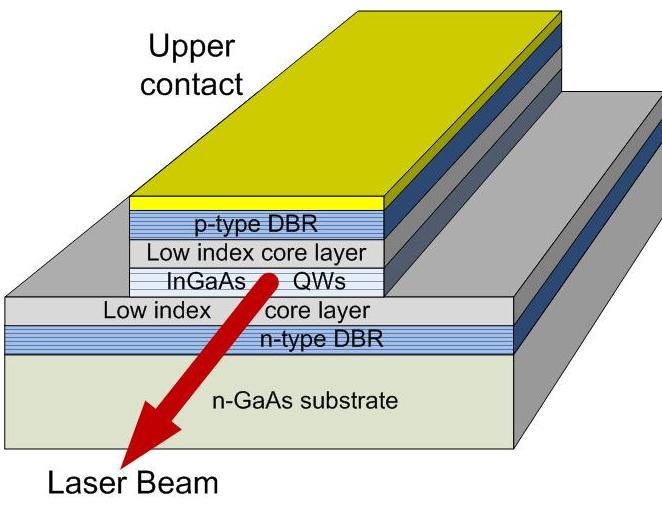
The substrate in a semiconductor laser serves as the foundation upon which the laser is built. It provides mechanical support and stability, as well as a surface for the deposition of the layers that make up the laser structure.
The substrate can affect the performance of a semiconductor laser in several ways. It can impact the crystal structure and quality of the layers grown on top, which can affect the electrical and optical properties of the laser. It can also affect the thermal conductivity and heat dissipation capabilities of the laser, which can impact its power output and efficiency.
Some common materials used as substrates for semiconductor lasers include gallium arsenide (GaAs), indium phosphide (InP), and gallium nitride (GaN). These materials have similar crystal structures to the semiconductor layers grown on top, allowing for a good match and minimizing defects.
Yes, the choice of substrate can affect the wavelength of a semiconductor laser. This is because the lattice constant of the substrate can influence the lattice constant of the layers grown on top, which in turn affects the bandgap and thus the emitted wavelength of the laser.
When selecting a substrate for a semiconductor laser, some key considerations include the lattice and thermal match to the layers grown on top, the desired emission wavelength, and the mechanical and thermal properties needed for the intended application. Cost and availability may also be factors to consider.