- #1
therayne
- 5
- 0
Sorry, the title is wrong, it's hoop rolling UP an incline
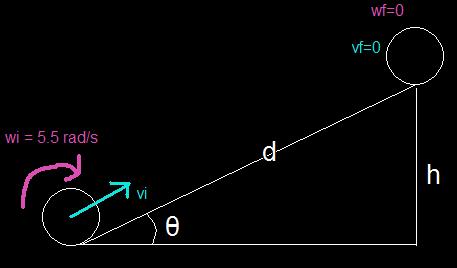
In a circus performance, a large 3.8 kg hoop
with a radius of 1.8 m rolls without slipping.
If the hoop is given an angular speed of
5.5 rad/s while rolling on the horizontal and is
allowed to roll up a ramp inclined at 17◦ with
the horizontal, how far (measured along the
incline) does the hoop roll? The acceleration
of gravity is 9.81 m/s2 .
Answer in units of m.
Known variables:
M=3.8 kg
R=1.8 m
wi = 5.5 rad/s
wf=0 rad/s
vi= wR
Angle A=17 degrees
h= d*sin(A)
d=?
*im using v and w at the center of mass, same for inertia
I = MR^2
rotational KE= (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2
KEf + Uf = KEi + Ui
0 + Mgh = (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2 + 0
Mgh = (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2
substitute:
h=d*sin(A)
w= v/R
I=MR^2
Mgd*sin(A) = (1/2)(MR^2)(v^2 / R^2) + (1/2)Mv^2
Mgd*sin(A) = (1/2)Mv^2 + (1/2) Mv^2
Mgd*sin(A) = Mv^2
d = v^2 / (g*sin(A))
using v=wR = 9.9
d= 234.17
Which is wrong.
I wasn't sure if i was supposed to include friction, does it even make sense for an object to roll without friction? I'm not sure, and I'm not sure how to even do the problem with friction. that would mean i would have to use torque right?
Thanks for the help.
Homework Statement
In a circus performance, a large 3.8 kg hoop
with a radius of 1.8 m rolls without slipping.
If the hoop is given an angular speed of
5.5 rad/s while rolling on the horizontal and is
allowed to roll up a ramp inclined at 17◦ with
the horizontal, how far (measured along the
incline) does the hoop roll? The acceleration
of gravity is 9.81 m/s2 .
Answer in units of m.
Known variables:
M=3.8 kg
R=1.8 m
wi = 5.5 rad/s
wf=0 rad/s
vi= wR
Angle A=17 degrees
h= d*sin(A)
d=?
*im using v and w at the center of mass, same for inertia
Homework Equations
I = MR^2
rotational KE= (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2
The Attempt at a Solution
KEf + Uf = KEi + Ui
0 + Mgh = (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2 + 0
Mgh = (1/2)Iw^2 + (1/2)Mv^2
substitute:
h=d*sin(A)
w= v/R
I=MR^2
Mgd*sin(A) = (1/2)(MR^2)(v^2 / R^2) + (1/2)Mv^2
Mgd*sin(A) = (1/2)Mv^2 + (1/2) Mv^2
Mgd*sin(A) = Mv^2
d = v^2 / (g*sin(A))
using v=wR = 9.9
d= 234.17
Which is wrong.
I wasn't sure if i was supposed to include friction, does it even make sense for an object to roll without friction? I'm not sure, and I'm not sure how to even do the problem with friction. that would mean i would have to use torque right?
Thanks for the help.