- #1
K-Manu
- 6
- 0
Hi,
I struggle to calculate the unit of the rate constant that is [m^3/sec]
rate constant of excitation by electron impact is as follows:
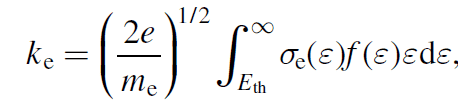
where, e=charge of electron [Coulomb], me=mass of electron [kg], ε=energy [eV], σe(ε)=cross section for electron impact [m^2], f(ε)=electron energy probability function [ev^-(3/2]. You can find the formula of rate constant in many works.
e. g. D. V. Lopaev, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50 (2017) 075202 (17pp) or site: file:///C:/Users/default.DESKTOP-PJAUC0O/Desktop/bolsigdoc0316.pdf
As my calculation, result might be C^(1/2)*m^3/sec, not m^3/sec, contrary to the results in the references.
What am I missing it?
I struggle to calculate the unit of the rate constant that is [m^3/sec]
rate constant of excitation by electron impact is as follows:
where, e=charge of electron [Coulomb], me=mass of electron [kg], ε=energy [eV], σe(ε)=cross section for electron impact [m^2], f(ε)=electron energy probability function [ev^-(3/2]. You can find the formula of rate constant in many works.
e. g. D. V. Lopaev, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50 (2017) 075202 (17pp) or site: file:///C:/Users/default.DESKTOP-PJAUC0O/Desktop/bolsigdoc0316.pdf
As my calculation, result might be C^(1/2)*m^3/sec, not m^3/sec, contrary to the results in the references.
What am I missing it?