- #1
GLD223
- 14
- 7
- Homework Statement
- Find the degrees of freedom of the system with the given PE. What are the variables of integration? Find the Lagrangian using the generalized coordinates.
- Relevant Equations
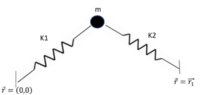
- ##PE = 1/2 * k_1 * R^2 + 1/2 * k_2 * (\vec{r} - vec{r_1})^2## note that ##r## and ##r_1## are vectors
So I think the mass can only move in two "coordinates" the axis of which the mass is connected to ##k_1## and the axis connecting it to ##k_2##. Therefore, the D.O.F is 2. I don't understand what it the meaning of "variables of integration" What does it mean?
Apart from that, I attempted to solve for the Lagrangian:
##T = 1/2 * m * v_m^2##
V is given
##v_m = d/dt(x_m)##
##x_m = 1/2 * \vec{r_1} + something* \hat{y} = 1/2 * r_1 * \hat{x} + something* \hat{y}##
I have no clue how to solve this. Any help would be appreciated
Apart from that, I attempted to solve for the Lagrangian:
##T = 1/2 * m * v_m^2##
V is given
##v_m = d/dt(x_m)##
##x_m = 1/2 * \vec{r_1} + something* \hat{y} = 1/2 * r_1 * \hat{x} + something* \hat{y}##
I have no clue how to solve this. Any help would be appreciated