- #1
zewei1988
- 22
- 0
Homework Statement
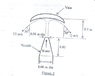
I was asked to find the mass flow rate and static pressure
Homework Equations
Bernoulli's equation
The Attempt at a Solution
I simply assumed that the area of the water jet hitting the vane is equals to the total area of water leaving the vane. I'm not sure if my assumption is true. From there I used Bernoulli's equation to find the speed of water leaving the nozzle, and hence the mass flow rate.
For the static pressure question, I felt that it should be p = rou*g*h + weight of vane/ area of nozzle.
I'm not sure if both are correct.