- #1
jonjacson
- 447
- 38
Imagine that we have an intertial system F, and there is an electric charge Q at the origin. Obviously the field is symmetric and spherical in this reference system.
Imagine another inertial system F' that is moving at constant speed v to the right respect to F, and at t=t'=0 both origins coincide.
After one second both systems will measure the intensity of the electric field at an sphere centered at the origin of coordinates (obviously we are talking about an sphere in their own systems of reference).
According to the measurements of F the field created by Q is spherical, What will be the field measured by F'?
My guess is this:
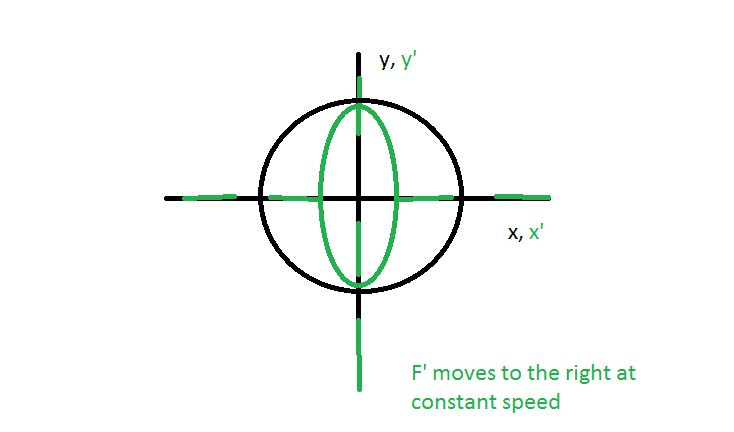
The points x' are contracted, and obviously closer to the charge Q at the origin.
We know that the instensity of the field is stronger if you are closer to the source, and weaker if you are further away, the system F' will perform measurements closer to the origin than F, Will F' get higher values for the intensity of the electric field?
Black is F, at rest, F' is green. I have represented in black an sphere in F, and an sphere in F' seen by F.
Imagine another inertial system F' that is moving at constant speed v to the right respect to F, and at t=t'=0 both origins coincide.
After one second both systems will measure the intensity of the electric field at an sphere centered at the origin of coordinates (obviously we are talking about an sphere in their own systems of reference).
According to the measurements of F the field created by Q is spherical, What will be the field measured by F'?
My guess is this:
The points x' are contracted, and obviously closer to the charge Q at the origin.
We know that the instensity of the field is stronger if you are closer to the source, and weaker if you are further away, the system F' will perform measurements closer to the origin than F, Will F' get higher values for the intensity of the electric field?
Black is F, at rest, F' is green. I have represented in black an sphere in F, and an sphere in F' seen by F.
Last edited: