- #1
bna10
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
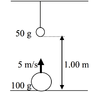
A ball of mass 100 g is projected straight up with a speed of 5 m/s from the floor. Another ball of mass 50 g is hung from the ceiling by a light string at a height of 1.00 m directly above the first ball, so that the projected ball collides elastically with it. Calculate the height above the floor to which the smaller ball will rise.
Homework Equations
1/2 M1V1i^2 = 1/2 M1V1f^2 + 1/2 M2V2f^2
The Attempt at a Solution
When I use the equation above it gives me two unknown variables V1f and V2f (after the collision). but I don't know what equation to use to figure out Δy.