- #1
LeoJakob
- 21
- 1
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
For the following conductor loop, determine the magnetic field along the ##z##-axis, which passes through the center of the conductor loop and is perpendicular to it.
The conductor loop consists of an infinitely long wire through which a constant current ##I## runs.
Is it possible to determine the magnetic fields in the different sections ## \vec B_i## with ## i \in \{ 1,2,3 \}## and then calculate the total field by ## \vec B= \sum \limits_{i=1}^3 \vec B_i##?
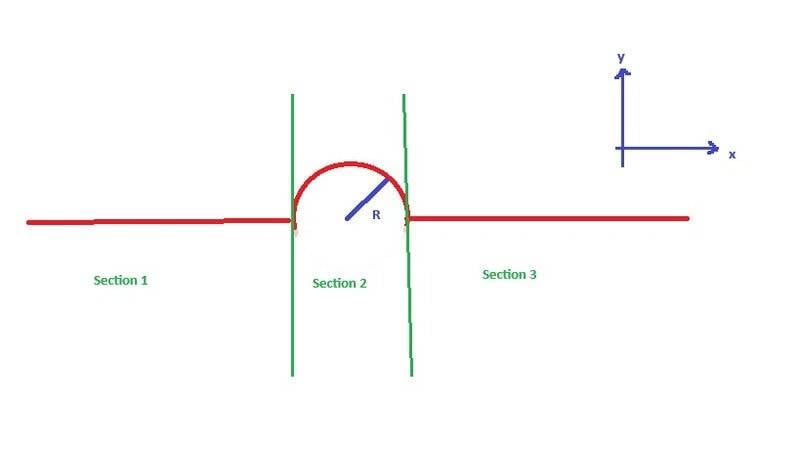
The conductor loop consists of an infinitely long wire through which a constant current ##I## runs.
Is it possible to determine the magnetic fields in the different sections ## \vec B_i## with ## i \in \{ 1,2,3 \}## and then calculate the total field by ## \vec B= \sum \limits_{i=1}^3 \vec B_i##?